 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...(800) 346-8274
Free Ground Shipping on Orders over $150!
Over 23,000 Items Discounts up to 40% off Retail
Types of Drill Bits
Types of Drill Bits
Our Newsletter
- Home
- Technical Info
- Types of Drill Bits
Types of Drill Bits
With dozens of drill bit types and thousands of sizes to choose from we'll explain the differences and help you choose the right drill bit for your application.
Anatomy of a drill bit:
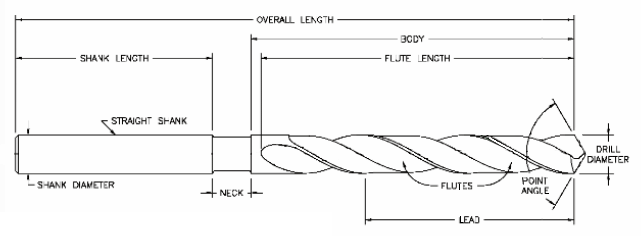
Materials used to make drill bits:
- Carbon Steel -
- High Speed Steel (HSS) -
- Cobalt Steel -
- Tool Steel w/ Carbide Tips -
- Solid Carbide -
Coatings used on drill bits:
- Black Oxide - The most economical coating. Black oxide adds corrosion protection, increases tempering and stress relieving of the bit, reduces galling and chip welding, and aids in retaining drilling lubricants. Black oxide is suitable for drilling iron and steel but is not recommended for drilling aluminum, magnesium, or similar materials.
- Bronze Oxide - Bronze oxide increases tempering and stress relieving of the bit and is generally used alone to visually identify cobalt steel or with black oxide to identify better grades of high speed steel.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN) - A more expensive coating that increases the hardness of the bit and provides a thermal barrier resulting in increased production rates and longer tool life in harder materials. TiN also provides the same benefits as black and bronze oxide. TiN coated bits are suitable for drilling iron and steel as well as aluminum, magnesium, etc.
Drill bits are generally classified as Twist Drill, Counterbore, Countersink, Flat Bottom Boring, and Specialty. On our web site we have divided these into two categories:
- Drill Bits - Normally used with hand held drills or drill presses fitted with standard chucks. These machines use a key to tighten or loosen the clamping mechanism.
- Boring Machine Bits - Typically used in automated machinery such as drill banks or CNC machines fitted with tool holders or single size collets. These machines require tools to assemble and disassemble the clamping mechanism. Many boring machine bits are available in right or left hand rotation.
*Note that most standard drill bits can be used in automated machinery (with the proper adapter) and most boring machine bits can be used in a portable drill or drill press (assuming the chuck is big enough). We have only organized them in this fashion to make selection easier.
 Twist Drills
Twist Drills
General Description: Twist drill bits are the most common type of drill bit and are used for everyday drilling in all types of material. They are also the most confusing due to the sheer number of size, tip, and material specifications.
Length Designations: The length of a twist drill has much to do with its rigidity - a shorter bit will be stronger and less likely to wander or break but may not have the reach needed for all jobs. Twist drill bits for use in automated machinery have an actual length specification (e.g. 4-1/2") while most (not all) twist drills for use in portable drills are graduated length and use a name to specify the length range:
- Jobber Length: These are the most common twist drills and are a good compromise between length and strength. Jobber drills vary in length according to their diameter and typically have a flute length of 9-14 times the cutting diameter, i.e. a 1/2" jobber drill has a flute length of 4-1/2" (nine times the diameter) with smaller drills having a larger ratio.
- Mechanics Length: Shorter than jobber drills, mechanics length drills are named as such because they fit into tighter spaces and are less likely to break while still allowing a reasonable flute length.
- Screw Machine Length: Also called "stubby length", these are the shortest common drill bits. Originally designed for screw machines, many people prefer these due to their high strength and added working clearance.
- Extra Length: These are extra long drill bits (up to 18") with flutes extending the entire length of the bit. Extra length drills can be very fragile and easily broken so it's usually best to drill as deep as possible with a jobber or shorter bit before switching to an extra length drill bit.
- Aircraft Extension: Similar in length to extra length bits, aircraft extension drill bits emphasize reach over cutting depth and have a shorter flute length (about the same as a jobber drill). This makes the bit much stronger and less susceptible to bending and breaking.
- Silver and Deming: More than a length specification, Silver and Deming drill bits are 6" long with a 3" flute length and a 1/2" diameter shank. All Silver and Deming bits are over 1/2" cutting diameter, ranging from 33/64" to 1-1/2", and are primarily intended for use in a drill press.
Size Designations: Common twist drills for use in portable drills, etc. are available in fractional inch, wire sizes, letter sizes, and metric decimal millimeter. Twist drills for use in automated machinery are only available in fractional inch and decimal millimeter. See our Drill Bit Size Chart for the breakdown of fractional, letter, and wire sizes.
Tip Styles: Twist drill bits are available with different tip styles to suit various applications as outlined below:
 Conventional Drill Point: This is the most common tip style as seen on everyday general purpose drills. The tip angle is usually 118 degrees but can vary from 90° to high angle "Plexi Point" for use in acrylics. Conventional drill point drills are the most economical and are easily re-sharpened. Suitable for wood, non-ferrous metals and mild steel.
Conventional Drill Point: This is the most common tip style as seen on everyday general purpose drills. The tip angle is usually 118 degrees but can vary from 90° to high angle "Plexi Point" for use in acrylics. Conventional drill point drills are the most economical and are easily re-sharpened. Suitable for wood, non-ferrous metals and mild steel. Split Drill Point: This is an advanced drill point that prevents walking and provides improved penetration with less effort. Available in 118 or 135 degree angles, split point drill bits are better for drilling in curved surfaces or in alloy steels. They are more expensive and more difficult to re-sharpen than standard drill points.
Split Drill Point: This is an advanced drill point that prevents walking and provides improved penetration with less effort. Available in 118 or 135 degree angles, split point drill bits are better for drilling in curved surfaces or in alloy steels. They are more expensive and more difficult to re-sharpen than standard drill points. V-Point: This is a special high angle tip used on drill bits for automated wood boring machines. V-point drills are used to create thru-holes in sheet stock for dowels or other assembly hardware.
V-Point: This is a special high angle tip used on drill bits for automated wood boring machines. V-point drills are used to create thru-holes in sheet stock for dowels or other assembly hardware. Brad Point: Designed for creating blind holes in wood and other soft materials for shelf pins, dowels, etc. Bradpoints are also used for thru-holes in CNC applications where a conventional drill point would penetrate the table below the panel. Bradpoints have spurs on the outer edges to prevent splintering and chipping of the surface material as well as a center spur to prevent walking as the bit penetrates the surface.
Brad Point: Designed for creating blind holes in wood and other soft materials for shelf pins, dowels, etc. Bradpoints are also used for thru-holes in CNC applications where a conventional drill point would penetrate the table below the panel. Bradpoints have spurs on the outer edges to prevent splintering and chipping of the surface material as well as a center spur to prevent walking as the bit penetrates the surface. Fishtail Point: These special drill points form a reverse "V" in the tip and are designed for drilling into a surface at an angle without walking. They are commonly used as center drills in counterbores for furniture assembly where panels must be joined at right angles.
Fishtail Point: These special drill points form a reverse "V" in the tip and are designed for drilling into a surface at an angle without walking. They are commonly used as center drills in counterbores for furniture assembly where panels must be joined at right angles. Taper Point: These drill bits have a very large taper, extending far up the drill which creates a tapered hole. Primarily used for old style wood screws.
Taper Point: These drill bits have a very large taper, extending far up the drill which creates a tapered hole. Primarily used for old style wood screws.
Flute Styles: Most twist drills have flutes to evacuate the chips at an unspecified angle, and are suitable for the majority of applications. Some specialty twist drills may be designated as "High Helix", "Fast Spiral" or "Low Helix", "Slow Spiral" for specific applications requiring higher or lower spindle speeds or feed rates.
Shank Styles: Twist drill bits designed for use in automated machinery have fixed diameter (usually 1/2" or 10mm) shanks, threaded shanks, or specialty shanks designed for certain machines. General purpose twist drills for use in portable drills have shanks the same diameter as the bit size (up to a certain diameter), larger diameter bits incorporate a reduced shank (either 1/4", 3/8" or 1/2") to fit into a standard drill chuck. Some bits have 3 flats on the shank to prevent spinning under high torque loads. Others have 1/4" hex shanks for use in a portable drill with a hex bit holder.
Materials: General purpose twist drills for use in portable drills are available in different grades of high speed steel as well as cobalt steel and solid carbide. Twist drill bits for automated machinery are available in carbon steel, high speed steel, carbide tipped, and solid carbide.
Coatings: General purpose drill bits are available with black oxide, bronze oxide, a combination of black and bronze oxide, and TiN coatings. Twist drills for automated machinery on our site are primarily for use in wood or plastics and are not coated.
 Counterbore Drill Bits
Counterbore Drill Bits
General Description: Counterbore drill bits create a flat bottom blind hole with a smaller diameter center hole that penetrates through the material. The purpose of a counterbore is usually to conceal the fastener head (by covering the hole) or provide a recess to prevent the fastener from protruding above the surface of the material being drilled. Counterbores on our site are designed for use in wood or plastics and are not intended for counterboring steel.
Tip Styles: The cutting tip of a counterbore drill consists of one or more flat blades extending from the center drill to the outer edge. Counterbores are available with or without spurs (teeth) at the outer diameter of the bit. Counterbores with spurs on the outer edge prevent chipping and splintering on wood or laminated surfaces.
Flute Styles: Some counterbores do not have flutes (except for the center drill) and simply shave away the material, others are designed similar to a twist drill with no tip angle and a replaceable center drill.
Shank Styles: Counterbores for use in hand-held drills typically clamp on to a standard twist drill and therefore have a straight shank the same diameter as the center drill. Counterbores for use in automated machinery have fixed diameter (usually 1/2" or 10mm) shanks, threaded shanks, or specialty shanks designed for certain machines.
Materials: Counterbores are available in Carbon Steel, High Speed Steel, or Carbide Tipped
Coatings: Counterbores on our site do not contain special coatings.
 Countersink Drill Bits
Countersink Drill Bits
General Description: Countersink drill bits create a tapered surface hole with a smaller center hole that penetrates through the material (some are available without a center drill for countersinking existing holes). The purpose of a countersink is to allow a tapered head fastener to sit flush with the surface of the material. Countersinks on our site are designed for use in wood or plastics and are not intended for counterboring steel.
Tip Styles: The cutting tip of a countersink drill consists of two or more flat blades extending from the center drill to the outer edge. Countersinks are made with angles from 60 to 120 degrees but those on our site are typically 82 or 90 degrees. For wood use many times the manufacturer does not specify the angle.
Flute Styles: Some countersinks do not have flutes (except for the center drill) and simply shave away the material, others are designed similar to a twist drill with a replaceable center drill.
Shank Styles: Countersinks for use in hand-held drills typically clamp on to a standard twist drill and therefore have a straight shank the same diameter as the center drill (some have 1/4" hex shanks for hand use in a bit holding screwdriver). Countersinks for use in automated machinery have fixed diameter (usually 1/2" or 10mm) shanks, threaded shanks, or specialty shanks designed for certain types of machines.
Materials: Countersinks are available in Carbon Steel, High Speed Steel, or Carbide Tipped
Coatings: Countersinks on our site do not contain special coatings.
 Flat Bottom Boring Bits
Flat Bottom Boring Bits
General Description: Flat bottom boring bits are similar to counterbores but do not include a center drill. These bits are designed to drill flat bottom blind holes for European style hinges, etc. Flat bottom boring bits are also used for drilling large diameter thru-holes without the plug that is typical when using a hole saw. These thru-hole bits are used for locks, door knobs, wiring holes, etc. Flat bottom boring bits on our site are designed for use in wood or plastics and are not intended for use in steel.
Common types of Flat Bottom Boring Bits include:
Tip Styles: The cutting tip of a flat bottom boring drill consists of one or more flat blades extending from the center to the outer edge. Flat bottom boring bits are available with or without spurs (teeth) at the outer diameter of the bit. Bits with spurs on the outer edge prevent chipping and splintering on wood or laminated surfaces. Some flat bottom boring bits also include a center spur to keep the bit from walking during the initial cut - Spade bits are a good example.
Flute Styles: Large flat bottom boring bits do not have flutes, they consist of only the cutting surface and the chips remain in the hole until the bit is removed.
Shank Styles: Most large flat bottom boring bits have a fixed size hexagonal shank. The hex shank prevents the bit from spinning in the chuck under excessive loads.
Materials: Flat bottom boring bits are available in Carbon Steel, High Speed Steel, or Carbide Tipped.
Coatings: Flat bottom boring bits on our site do not contain special coatings.
Specialty Drill Bits
General Description: Specialty drill bits are any bit that doesn't fall into one of the four categories above. These bits include:
-
 Plug Cutters - Essentially a hole saw without a center drill, these bits are designed to cut round plugs from lumber or other stock that are used to fill a counterbore after fastening the parts. After gluing the plug into the counterbore, the plug is then cut and sanded flush to conceal the hole. Plug cutter bits are measured by their inside diameter (the size of the plug that will be left) and are not meant to drill completely through the stock. Instead, the stock is drilled to a depth slightly deeper than the hole to be filled and the plug is popped out using a small screwdriver or other tool. Plug cutters are almost always used in a hand held drill.
Plug Cutters - Essentially a hole saw without a center drill, these bits are designed to cut round plugs from lumber or other stock that are used to fill a counterbore after fastening the parts. After gluing the plug into the counterbore, the plug is then cut and sanded flush to conceal the hole. Plug cutter bits are measured by their inside diameter (the size of the plug that will be left) and are not meant to drill completely through the stock. Instead, the stock is drilled to a depth slightly deeper than the hole to be filled and the plug is popped out using a small screwdriver or other tool. Plug cutters are almost always used in a hand held drill. -
 Glass and Tile Drills - Used to drill holes (usually for fasteners) in non-tempered glass, tile, and similar materials. These bits feature carbide tips and straight shanks that can be used in either hand drills or automated machinery.
Glass and Tile Drills - Used to drill holes (usually for fasteners) in non-tempered glass, tile, and similar materials. These bits feature carbide tips and straight shanks that can be used in either hand drills or automated machinery. -
 Masonry Drills - Used to drill holes in concrete, brick, etc. using a special "hammer drill" which pounds the drill bit as it rotates. A threaded anchor is usually installed if the hole is to be used to attach objects to the surface. Masonry drills have carbide tips and either standard or high helix flutes depending on the intended use. They are typically coated with black oxide to prevent corrosion and feature shanks that are either the same size as the bit or reduced diameter to fit the portable drill chuck.
Masonry Drills - Used to drill holes in concrete, brick, etc. using a special "hammer drill" which pounds the drill bit as it rotates. A threaded anchor is usually installed if the hole is to be used to attach objects to the surface. Masonry drills have carbide tips and either standard or high helix flutes depending on the intended use. They are typically coated with black oxide to prevent corrosion and feature shanks that are either the same size as the bit or reduced diameter to fit the portable drill chuck. -
 Augers - Designed to bore somewhat large holes deeply into wood or other similar materials. Auger tips feature a protruding tapered screw that helps to pull the bit into the wood with one or two cutting edges similar to a counterbore and may include outer spurs. The flutes of an auger drill bit are extra large to pull the chips up and out of the hole. Augers are normally used in hand held drills and the shank may be round or hexagonal.
Augers - Designed to bore somewhat large holes deeply into wood or other similar materials. Auger tips feature a protruding tapered screw that helps to pull the bit into the wood with one or two cutting edges similar to a counterbore and may include outer spurs. The flutes of an auger drill bit are extra large to pull the chips up and out of the hole. Augers are normally used in hand held drills and the shank may be round or hexagonal. -
 Annular Cutters - Used to drill larger thru-holes in metal (7/16" and up), these bits require a special machine. Similar to a hole saw, annular cutter bits cut the outer diameter of the hole and leave a solid center slug. This creates a much more efficient drilling process with burr-free holes in tubing, sheet metal and iron bar stock. Annular cutter bits on our site are made from Cobalt High Speed Steel.
Annular Cutters - Used to drill larger thru-holes in metal (7/16" and up), these bits require a special machine. Similar to a hole saw, annular cutter bits cut the outer diameter of the hole and leave a solid center slug. This creates a much more efficient drilling process with burr-free holes in tubing, sheet metal and iron bar stock. Annular cutter bits on our site are made from Cobalt High Speed Steel.





